Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis (HGE) in dogs is a serious condition. It involves a sudden onset of bloody diarrhea and vomiting. While it can be frightening, early recognition and prompt veterinary care are crucial for a successful recovery.
In this blog post, we’ll discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatment of HGE. We’ll also provide tips on how to prevent this condition and what to do if your dog is experiencing symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors of HGE in Dogs
Potential Triggers and Causes of HGE
While the exact cause of hemorrhagic gastroenteritis in dogs is often unknown, several factors may contribute to its development:
- Dietary indiscretion: Consuming spoiled food, foreign objects, or sudden dietary changes can trigger HGE.
- Stress: Stressful events like moving, introducing a new pet, or traveling can increase the risk.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can contribute to HGE.
While any dog can be affected by HGE, young adult dogs, especially smaller breeds, may be more susceptible.
Recognizing the Symptoms of HGE
Key Symptoms to Watch For
If you notice the following symptoms in your dog, it may be a sign of HGE:
- Severe diarrhea: Frequent, watery, or bloody stool
- Vomiting: May be frequent and forceful
- Lethargy: Decreased energy levels and weakness
- Dehydration: Dry gums, decreased skin elasticity, and decreased appetite
- Abdominal pain: Your dog may show signs of abdominal discomfort, such as restlessness or guarding their belly
When to Seek Veterinary Care
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek immediate veterinary care. Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis in dogs can quickly lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, which can be life-threatening. Early intervention is essential to prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery.
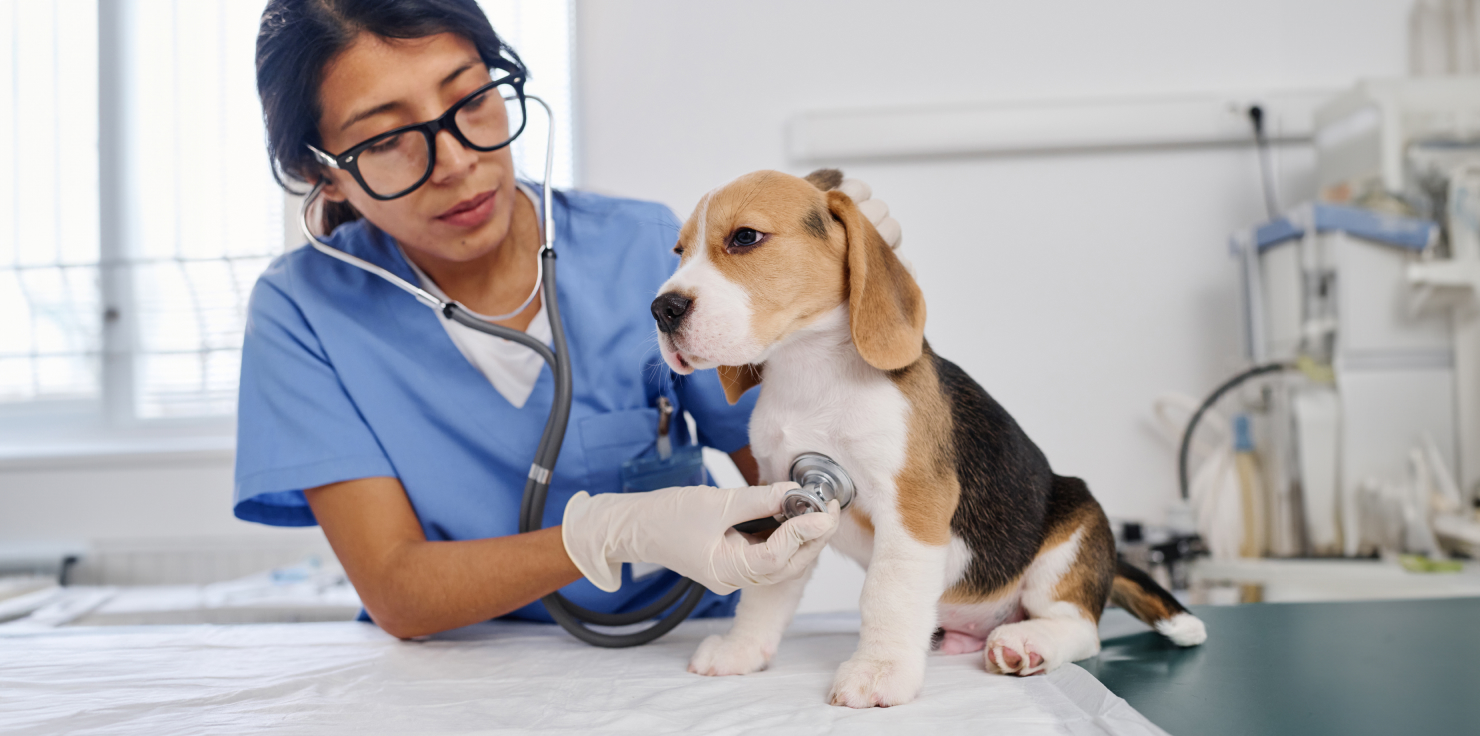
Diagnosing HGE in Dogs
Veterinary Examination and Tests
To diagnose HGE, your veterinarian will perform a thorough physical examination, including checking your dog’s vital signs and assessing their hydration status. They may also recommend the following tests:
- Blood tests: To evaluate blood cell counts, electrolyte levels, and organ function.
- Stool analysis: To identify parasites or other abnormalities.
Differential Diagnosis
It’s important to rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. Some conditions that may mimic hemorrhagic gastroenteritis in dogs include:
- Parvovirus: A highly contagious viral infection that can cause severe vomiting and diarrhea.
- Intestinal parasites: Parasites like worms or coccidia can cause digestive issues.
- Inflammatory bowel disease: A chronic inflammatory condition of the intestines.
A thorough veterinary examination and diagnostic tests can help differentiate HGE from other conditions.
Treatment Options for HGE
Hospitalization and Fluid Therapy
Dogs with HGE often require hospitalization to receive aggressive fluid therapy. IV fluids help to correct electrolyte imbalances, maintain blood pressure, and prevent dehydration, which is a major concern in HGE.
Medications for Symptom Management
In addition to fluid therapy, your veterinarian may prescribe medications to manage symptoms:
- Anti-nausea medications: To control vomiting and reduce discomfort.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat underlying bacterial infections.
- Pain relievers: To alleviate pain and discomfort.
Dietary Management During Recovery
Once your dog has stabilized, your veterinarian may recommend a bland diet to help soothe the digestive tract. A bland diet typically consists of easily digestible foods like boiled chicken and rice. It’s important to follow your veterinarian’s specific instructions for feeding your dog during their recovery. As your dog improves, you can gradually transition them back to their regular diet.
Home Care and Support for Dogs with HGE
Ensuring Proper Hydration
Once your dog is discharged from the hospital, it’s crucial to ensure they stay hydrated.
- Offer small, frequent amounts of water: Avoid overwhelming your dog with large bowls of water.
- Use a syringe or dropper: If your dog is reluctant to drink, you can use a syringe or dropper to administer water directly into their mouth.
- Monitor for dehydration: Signs of dehydration include dry gums, decreased skin elasticity, and lethargy.
Monitoring Your Dog’s Recovery
As your dog recovers at home, it’s important to monitor them closely for any signs of relapse:
- Watch for recurring vomiting or diarrhea.
- Monitor their appetite and energy levels.
- Keep a stress-free environment. Avoid stressful situations that can trigger a relapse.
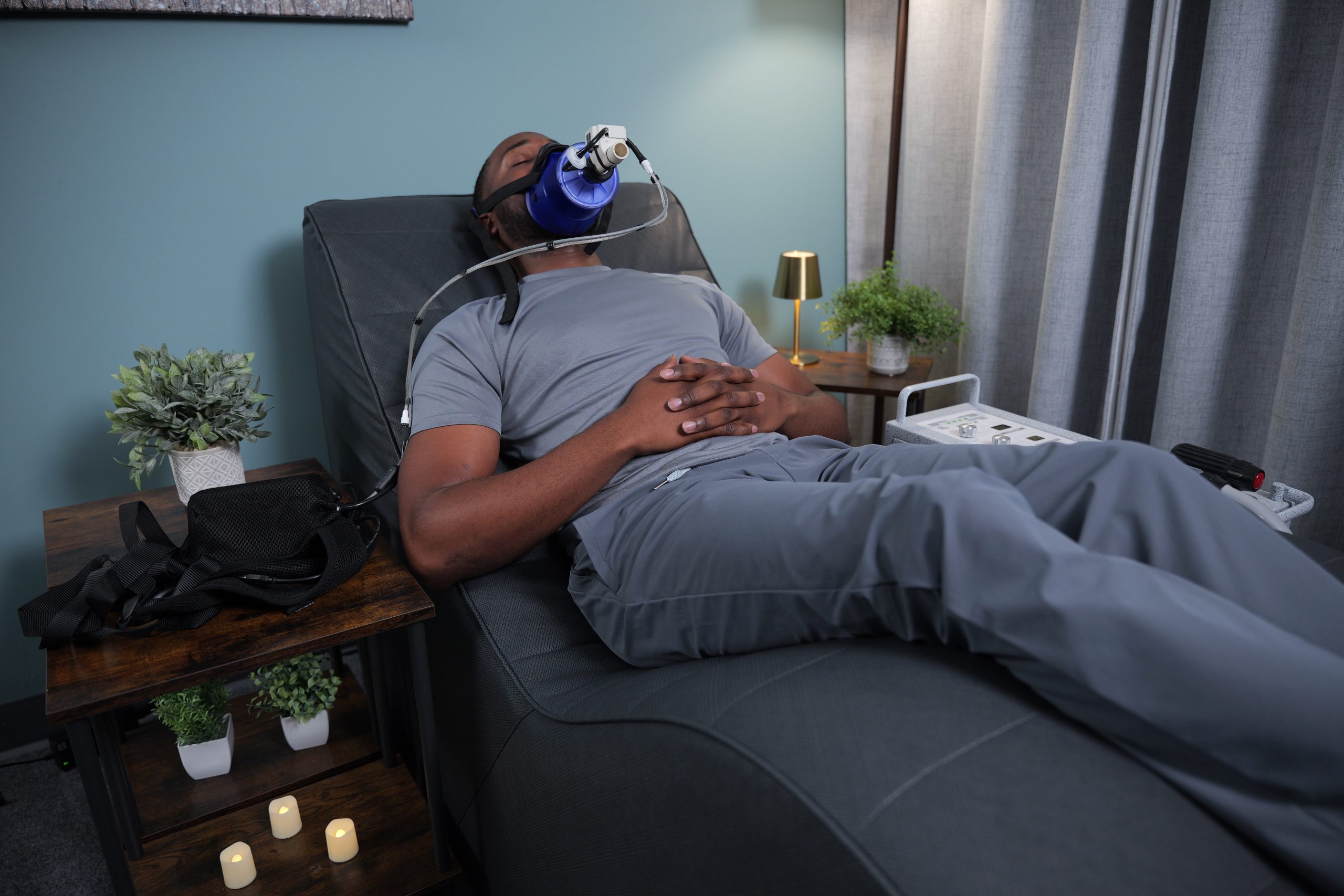
Alternative Therapies for Recovery Support
In addition to traditional veterinary care, you may consider exploring complementary therapies to support your dog’s recovery.
PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy is a non-invasive therapy that may help promote self-healing and recovery. By optimizing cellular function, PEMF therapy may help your dog recover more quickly and comfortably.
It’s important to note that PEMF therapy should be used as a complementary therapy and not as a replacement for veterinary care. Always consult with your veterinarian to determine if PEMF therapy is appropriate for your dog’s specific needs.
Learn more about the science, mechanisms, and powerful benefits of PEMF here.
Preventing Recurrence of HGE in Dogs
Diet and Feeding Recommendations
- Maintain a stable diet: Avoid sudden changes in your dog’s diet.
- Portion control: Avoid overfeeding, as it can lead to digestive upset.
- Limit treats: Excessive treats can disrupt your dog’s digestive system.
- Avoid foods that can trigger HGE: These may include rich foods, fatty foods, or spoiled food.
Managing Stress and Anxiety
- Create a calm environment: Reduce stress-inducing factors like loud noises or sudden changes in routine.
- Provide mental and physical stimulation: Engage your dog in activities they enjoy, such as playing or training.
- Consider calming aids: Consult with your veterinarian about calming supplements or medications.
Routine Health Checks
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for maintaining your dog’s overall health and preventing future episodes of HGE. During these visits, your veterinarian can:
- Monitor your dog’s weight and body condition.
- Check for any signs of illness.
- Administer preventative medications, such as flea and tick preventatives.
- Address any concerns or questions you may have.
Conclusion
Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis in dogs can be a serious condition, but with prompt veterinary care and proper management, most dogs can recover fully. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for HGE, you can take steps to protect your dog’s health.
Remember to consult with your veterinarian for personalized advice and to explore complementary therapies like PEMF under their guidance. By working together, you can help your dog recover from HGE and prevent future episodes.